Cgroups and Containers
Cgroups is a Linux kernel feature to limit, account and isolate resource usage of process groups. Cgroups allow you to allocate resources—such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, or combinations of these resources—among user-defined groups of tasks (processes) running on a system.
What is Cgroups?
Cgroups is a Linux kernel feature to limit, account and isolate resource usage of process groups. Cgroups allow you to allocate resources—such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, or combinations of these resources—among user-defined groups of tasks (processes) running on a system. You can monitor the cgroups you configure, deny cgroups access to certain resources, and even reconfigure your cgroups dynamically on a running system.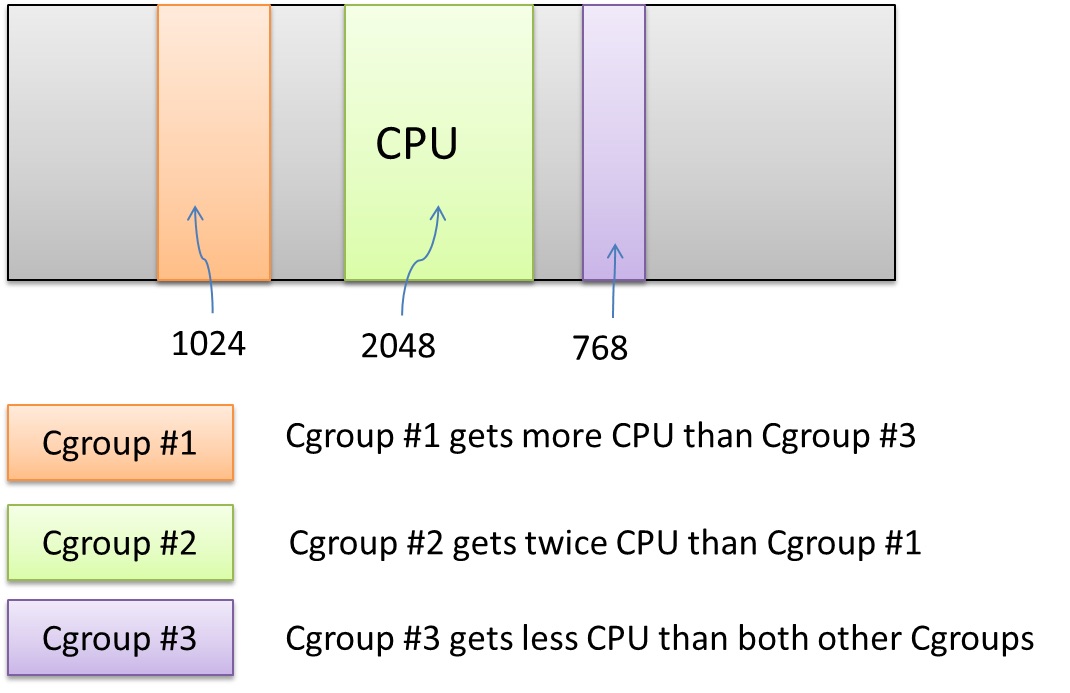
The above figure describes the CPU shares limitation using Cgroups. We can see that three Cgroups use chunks of CPU. Cgroup #1’s share is 1024. Cgroup #2’s share is greater than both other Cgroups, so it’ll get more CPU than both others. Cgroup #3 will get least CPU share.
Subsystems of Cgroups:
Other than CPU subsystem, there are eight other subsystems available. Let’s have a look at all the Cgroups subsystems in brief:
- blkio — this subsystem sets limits on input/output access to and from block devices such as physical drives (disk, solid state, USB, etc.).
- cpu — this subsystem uses the scheduler to provide cgroup tasks access to the CPU.
- cpuacct — this subsystem generates automatic reports on CPU resources used by tasks in a cgroup.
- cpuset — this subsystem assigns individual CPUs (on a multicore system) and memory nodes to tasks in a cgroup.
- devices — this subsystem allows or denies access to devices by tasks in a cgroup.
- freezer — this subsystem suspends or resumes tasks in a cgroup.
- memory — this subsystem sets limits on memory use by tasks in a cgroup, and generates automatic reports on memory resources used by those tasks.
- net_cls — this subsystem tags network packets with a class identifier (classid) that allows the Linux traffic controller (tc) to identify packets originating from a particular cgroup task.
- net_prio — this subsystem provides a way to dynamically set the priority of network traffic per network interface.
- ns — the namespace subsystem.
Features:
Now, let’s discuss about features provided by Cgroups. Cgroups provides following features:
- Resource Limitation: Groups can be set to not exceed a resource limitation. This limitation includes memory limit, file system cache limit, disk I/O throughput limitation etc.
- Prioritization: Some groups may get a larger share of CPU, disk I/O throughput etc.
- Accounting: We can measure how much resources certain systems use.
- Isolation: Separate namespaces are provided for groups, so they remain fully exclusive to each other. The groups cannot see each other’s processes, network connections etc.
- Control: We can freeze groups, checkpoint and restart the container.
Cgroup come readily available with linux kernel source.